

- #HOW TO CHANGE EFI SYSTEM PARTITION TO FAT32 UPDATE#
- #HOW TO CHANGE EFI SYSTEM PARTITION TO FAT32 PROFESSIONAL#
- #HOW TO CHANGE EFI SYSTEM PARTITION TO FAT32 DOWNLOAD#
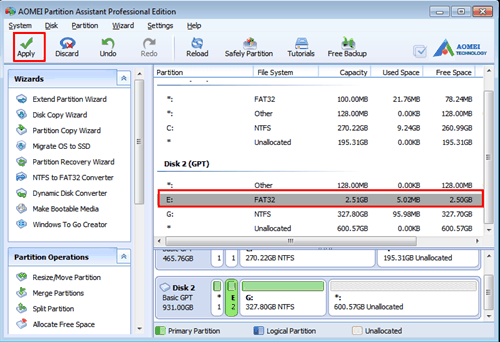
If you need a FAT32 partition to boot with EFI for example, then you should use something like /boot/efi/ to mount the FAT32 partition there, which will not be managed by dpkg, and use kernel postinst hooks to copy any required files, in a similar way as would be done to create an initramfs. If you are installing on a NFS root, and locking does not work, make sure rpc.lockd (or its equivalent) is running. renaming directories atomically inside the same parent directory (with rename(2))Īs such, filesystems like FAT32 or AFS are not supported for dpkg managed content. replacing files currently open (and being executed) (with rename(2)). It used to not even have a 3 line grub.cfg in other labels, now it does, but something internally is still. But whenever I use a -L label different than Ubuntu, it still boots from the /EFI/ubuntu/grub.cfg, so make sure you have that also and it is correct. file-region locking ( fcntl(2) with F_SETLK 134591, 149491), sudo efibootmgr -c -L 'Ubuntu-NVMe' -l 'EFIubuntushim圆4.efi' -d /dev/nvme0n1 -p 1. returning the symlink length in stat(2) st_size, Q: What are the filesystem requirements by dpkg?Ī: The filesystems are expected to have POSIX semantics.ĭpkg expects to operate on filesystems that support at least: Its resize/move partition feature now fully supports to extend EFI partition and shrink EFI system partition on GPT disk easily.
#HOW TO CHANGE EFI SYSTEM PARTITION TO FAT32 DOWNLOAD#
Please choose a different file system, such as ext2". Download EaseUS Partition Master to resize (shrink or extend) EFI system partition in Windows 11/10/8/7/XP/Vista. Debian installer will complain saying: "The file system type fat 32 cannot be mounted on /boot, because it is not a fully-functional Unix file system. It is not possible to use an EFI system partition (FAT32) for /boot on Debian. How can I reproduce this on Debian? Is it possible at all? Thanks!Įdit 2: Deleted what I though it was the solution. Tip: UEFI systems can use the EFI system partition for /boot On arch - dmcrypt there's a tip that says: I was able to successfully do that on Arch Linux, but under Debian I wasn't so lucky. I have a VERY specific condition and I need this to achieve my requirements. I love Linux and its community and would like to know if it's possible to place /boot under my EFI partition (FAT32) on Debian.
#HOW TO CHANGE EFI SYSTEM PARTITION TO FAT32 PROFESSIONAL#
After completing all the operations you want to perform, click the "Exit" button to close the EFI System Partition Explorer.Īs a professional EFI system partition management tool, EasyUEFI provides an EFI system partition Explorer, which can help you explore and write files to an EFI System Partition (ESP) in Windows 10/8.1/8/7 and Windows Server 2019/2016/2012/2008.Hi, I've already made this post on r/debian and I think I can gain some more insights here. Now you can explore this EFI system partition and write files to the EFI system partition. look for volume id of the 500mb partition ( x ). You can manually unmount by this commandlets.
#HOW TO CHANGE EFI SYSTEM PARTITION TO FAT32 UPDATE#
Most Update seem to fail, sometimes a reboot helps to unmount the partition. Select the EFI System Partition (ESP) you want to explore in the disk/partition list, then click the "Open" button to open the EFI System Partition Explorer. To apply the update the efi partition has to be mounted. Click the 'Explore EFI System Partition' button. Run EasyUEFI, then click the 'Manage EFI System Partition' button. Tutorial to Explore and Write files to EFI system partition (ESP) in Windows 10/8.1/8/7 and Windows Server 2019/2016/2012/2008. As a professional EFI system partition management tool, EasyUEFI provides an EFI system partition Explorer, which can helps users explore and write files to ESP partition. You can use diskpart to assign a drive letter to ESP partition and then use DOS commands to read and write the ESP partition, but this is very difficult for many users. Therefore we cannot explore and write files to an EFI system partition (ESP) in Windows. To prevent accidents, Windows does not assign drive letters for the ESP partitions by default and users cannot assign a drive letter to an ESP partitions in the disk manager. The EFI System Partition (ESP) contains the boot loader programs for all operating systems installed on the computer, and abnormally deleting these files may cause the operating system to fail to start properly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
